| |
What is the menstrual cycle (uterine cycle)?
Menstruation is part of the menstrual cycle, which prepares your body for pregnancy each month.
Between every 20 to 40 days your hormones will cause the ovary to release a mature egg (also called ovum, oocyte, or female gamete) This egg will travel through the fallopian tube, hoping to meet a male sperm cell for fertilization to occur. The cycle in which the immature egg in the follicle becomes mature is known as the ovarian cycle. The release of the mature egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube is known as ovulation.
What happens during the menstrual cycle?
The cycle is counted from the first day of one period to the first day of the next period. It is all controlled tightly by your sex hormones from your endocrine system.
Let's see the diagrams below showing the parts of the reproductive organ:
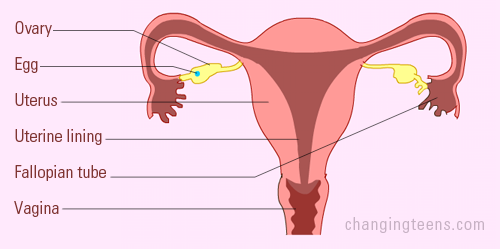
 At about day 14 of a typical 28-day cycle, the egg leaves the ovary. This is called ovulation.The process is controlled by your sex hormones. It starts with the release of an egg (ovum, about the size of 1/10 of a poppy seed) in one of your fallopian tubes. At about day 14 of a typical 28-day cycle, the egg leaves the ovary. This is called ovulation.The process is controlled by your sex hormones. It starts with the release of an egg (ovum, about the size of 1/10 of a poppy seed) in one of your fallopian tubes.
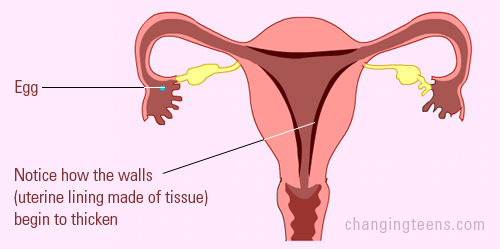
 As the egg starts to move, your body increases hormones (estrogen), making the lining of the uterus (womb) grow and thicken with blood and nutrients. (This is a natural way of your body telling the uterus to get ready for pregnancy just in case the egg is fertilized) As the egg starts to move, your body increases hormones (estrogen), making the lining of the uterus (womb) grow and thicken with blood and nutrients. (This is a natural way of your body telling the uterus to get ready for pregnancy just in case the egg is fertilized)
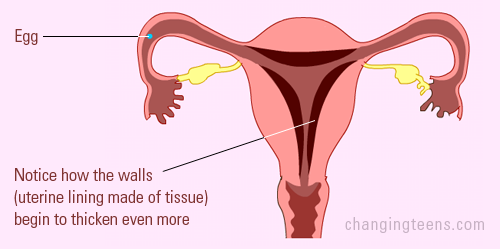
 The egg then travels through the Fallopian tube to the uterus. A woman is most unlikely to get pregnant during the three days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation if there is a sexual activity. Note that if fertilization occurs, the egg will attach itself in the walls of the womb and begin its growth. The egg then travels through the Fallopian tube to the uterus. A woman is most unlikely to get pregnant during the three days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation if there is a sexual activity. Note that if fertilization occurs, the egg will attach itself in the walls of the womb and begin its growth.
 Usually the egg is not fertilized, and it dissolved. This makes your hormone level drop, and the thickened tissues and lining of the uterus is shed, in the form of blood, flowing out of the vagina. Usually the egg is not fertilized, and it dissolved. This makes your hormone level drop, and the thickened tissues and lining of the uterus is shed, in the form of blood, flowing out of the vagina.
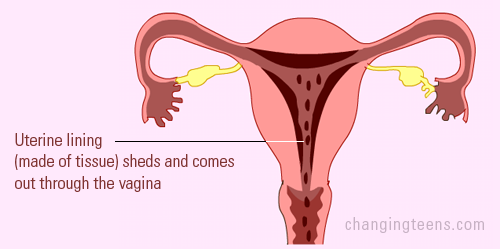
 The average cycle length is 28 days but different girls can have different length cycles and different period flows. The average cycle length is 28 days but different girls can have different length cycles and different period flows.
 
|
|
